For understand Heap Sort we first understand some concept such as:
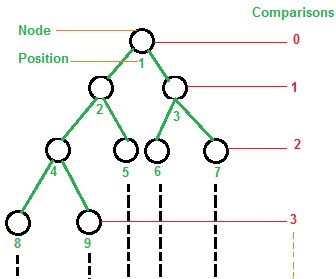
BINARY TREE : Binary tree is tree which have at most (maximum) two child one is right side and another is left side of element. In binary tree top most element is called Parent / Root node and below of root node is called Child Node. Connecting line is called link. Show in diagram below.👇
In heap sort first we insert the element in hear tree i.e first we create heap tree by arranging elements and than for sorting we first delete the element from the last inserted element. After that we get list of deleted elements which is in an order or we can say that those elements are sorted automatically.
In short we can say that two step perform for heap sort:
STEP 1: Create Heap Tree
STEP 2: Delete last inserted element from tree.
Now we understand heap tree with the help of an example:
Suppose we want to sort following elements such as:
15 , 25 , 30 , 17 , 80 , 29 , 95
Now we first create heap tree.
CASE 1: Take first element i.e 15 and insert into tree. we get following tree.
Now note single element is always a heap tree.CASE 2: Take second element i.e 25 and insert it into second position in tree.But we know that in heap tree parent is always greater than child.So before inserting we must check new element 25 to previous element 15 with condition ( P > C) i.e (15 > 25) condition is false so we must perform swapping between them and check " Is the tree is a heap tree ? " , answer is yes so the tree is following.
CASE 3: Take third element i.e 30 and insert it into third position in tree.But we know that in heap tree parent is always greater than child.So before inserting we must check new element 30 to parent element i.e 25 with condition ( P > C) i.e (25 > 30) condition is false so we must perform swapping between them and check " Is the tree is a heap tree ? " , answer is yes so the tree is following.
CASE 4: Take forth element i.e 17 and insert it into forth position in tree.But we know that in heap tree parent is always greater than child.So before inserting we must check new element 17 to parent element i.e 15 with condition ( P > C) i.e (15 > 17) condition is false so we must perform swapping between them and check " Is the tree is a heap tree ? " , answer is yes so the tree is following.
CASE 5: Take fifth element i.e 80 and insert it into fifth position in tree.But we know that in heap tree parent is always greater than child.So before inserting we must check new element 80 to parent element i.e 17 with condition ( P > C) i.e (17 > 80) condition is false so we must perform swapping between them and Now we place 80 in second position and again check whether it is a heap tree or not , we see it violet heap tree condition because their is again need to check second position and first position element i.e 80 and 30 , check ( P > C) i.e (30 > 80) condition is false so again we perform swapping between them and again check " Is the tree is a heap tree ? " , answer is yes so the tree is following.
CASE 6: Take sixth element i.e 29 and insert it into sixth position in tree.But we know that in heap tree parent is always greater than child.So before inserting we must check new element 29 to parent element i.e 25 with condition ( P > C) i.e (25 > 29) condition is false so we must perform swapping between them and again check " Is the tree is a heap tree ? " , answer is yes so the tree is following.
CASE 7: Take seventh element i.e 95 and insert it into seventh position in tree. But we know that in heap tree parent is always greater than child.So before inserting we must check new element 95 to parent element i.e 29 with condition ( P > C) i.e (29 > 95) condition is false so we must perform swapping between them and again check " Is the tree is a heap tree ? " , answer is No and the tree is following.
Again check condition ( P > C) i.e (80 > 95) condition is false so we must perform swapping between them and the tree is following.
Again check " Is the tree is a heap tree ? " , answer is Yes and the tree is following. All the element are inserted and the tree is a final heap tree.
Now shorting procedure take place in the above 👆 heap tree.
For sorting list start deleting element from last position i.e 7.
CASE 1: In first case we see that 95 is largest element so we first place the 95 in last position i.e 7 by swapping between 29 & 95 we get.
In the above tree 👆 we delete 95 and than it become the first sorted element.The tree will we.
Now again check the above tree 👆 is a heap tree the answer is no, than we first make it heap tree so swapping done between those elements which not satisfy heap tree condition. i.e element 29 in 1-position and element 80 in 3-position. we get following tree.
Note for deletion always swapping between Root element and element of last position.
In the above tree 👆 we delete 80 and than it become the second sorted element.The tree will we.
Now again check the above tree 👆 is a heap tree the answer is no, than we first make it heap tree so swapping done between those elements which not satisfy heap tree condition. i.e element 25 in 1-position and element 30 in 2-position. we get following tree.
Similarly same procedure is apply with other elements.
Now we collect the deleted elements i.e: 95, 80 , 30 , 29 , 25 , 17 , 15 they are in sorted in descending order.
PROCEDURE OF HEAP SORT IN C
void heapsort ( int a[50], int n)
{
int temp;
while (n > 1)
{
createheap ( a ,n ); // CALL HEAP CREATE FUNCTION
temp = a[1];
a[1] = a[n];
a[n] = temp;
n--;
}
}
void createheap ( int a[50], int n )
{
int i , c , p , temp ;
for ( i=2 ; i<=n ; i++ )
{
c = i;
p = c/2;
while ( c > 1 && a[c] > a[p] )
{
temp = a[c];
a[c] = a[p];
a[p] = temp;
c = p;
p = c/2;
}
}
}
ALGORITHM FOR PROCEDURE HEAP SORT (A, N)
A is an array with N- elements.
STEP 1: WHILE N > 1
STEP 2: CALL SUB PROCEDURE CREATEHEAP (A,N)
STEP 3: TEMP = A[1]
STEP 4: A[1] = A[N]
STEP 5: A[N] = TEMP
STEP 6: N = N-1
STEP 7: END WHILE
STEP 8: END
ALGORITHM FOR SUB PROCEDURE CREATEHEAP (A,N)
A is an array with N elements.
STEP 1: FOR I=2 TO N DO
STEP 2: C=I [ where C stands for child position ]
STEP 3: P=C/2 [ where P stands for parent position ]
STEP 4: WHILE C >1 AND A[C] > A[P]
STEP 5: TEMP = A[C]
STEP 6: A[C] = A[P]
STEP 7: A[P] = TEMP
STEP 8: C = P
STEP 9: P = C/2
STEP 10 : END WHILE
STEP 11: NEXT I
STEP 12: END
EVOLUTION OF HEAP SORT
In heap sort to insert Nth key into a heap tree it need at most (log2N) comparisons. So to sort array with N elements heap sort needs ( Nlog2N) comparisons with complexity (Bigo of) O(nlog2n)
Friends I explain all concept and procedure of HEAP SORT. I hope this post is useful for you.We will meet in next post. 👀👍